Claude for work: How to use Claude Skills and Artifacts to 10x team efficiency


Learn how to use Claude Skills and Artifacts to automate team workflows. Step-by-step guide to building reusable tools without code for 10x efficiency.
All large language models (LLMs)—Claude, ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, and others—have their own strengths. If you’re a founder, manager, or team lead, the real question isn’t “Which model is the smartest?” but: “Which tool helps my team get work done faster and more reliably?”
Claude is a strong candidate when:
- You work with long documents or complex processes (e.g. sales discovery, contracts, technical docs).
- You care about structured, repeatable workflows rather than one-off clever replies.
- You want your AI setup to look less like “random prompts in a chat window” and more like a system your team can trust.
In this article, we’ll walk through:
- Three key benefits of using Claude for work
- What Claude Skills are and how to build your first one
- What Claude Artifacts are and when to use them
- How Skills and Artifacts fit into your wider AI stack (alongside tools like ChatGPT and Gemini)
TL;DR
- Claude is a strong option for teams that want to automate repeatable work instead of rewriting prompts every day.
- Claude Skills let you turn your processes, playbooks, and expertise into reusable building blocks that Claude can load automatically when they’re relevant.
- Claude Artifacts turn conversations into shareable tools and mini-apps that teams can use again and again, without code.
- Together, Skills + Artifacts help you move from “we’re experimenting with AI” to “AI quietly runs part of our workflows,” especially in areas like sales follow-ups, customer support, operations, and documentation.
- You don’t have to choose one model forever. Claude is often a great fit when you want structured, repeatable workflows, while models like ChatGPT or Gemini might still be your go-to for other jobs.
Three benefits of using Claude
Claude stands out for many reasons, three of them being:
- Massive context window — Claude can handle hundreds of pages of input without losing track. Ideal for legal documents, medical records, or anything multi-layered.
- More thoughtful, in-depth responses — Claude tends to stay closer to the source materials, is less prone to hallucinations, and is well-suited for explanations, analysis, and reasoning.
- Skills + Artifacts = an automated workflow that always brings results — Unlike Gemini or ChatGPT’s Custom GPTs, Claude combines persistent memory, code execution, and live tools in one ecosystem.
To recap, here’s how Claude often helps teams:
- Handles big, messy inputs → great for docs, transcripts, and multi-step reasoning
- Produces in-depth, structured outputs → less hand-holding, more useful drafts
- Gives you tools (Skills + Artifacts) to build systems → not just isolated chats
Three features that set Claude apart
You spend more time correcting the AI than doing the work. Claude Skills and Artifacts eliminate that friction.
Claude Skills are reusable capabilities that load on demand, like expert assistants that activate only when needed. Each one sits dormant until Claude recognizes it's relevant to your task. This saves token costs and execution time—up to 90% in some workflows.
Claude Artifacts are live-preview mini-apps you build directly in the interface. Unlike ChatGPT Canvas, Artifacts can embed AI features inside the app itself. You can create a sales tool that analyzes call transcripts, extracts pain points, and generates follow-up emails—all powered by Claude's API in real time.
Your team gets consistent outputs without micromanaging every prompt. Faster ROI. Fewer errors. Scalable automation that enables your team to work better and faster.

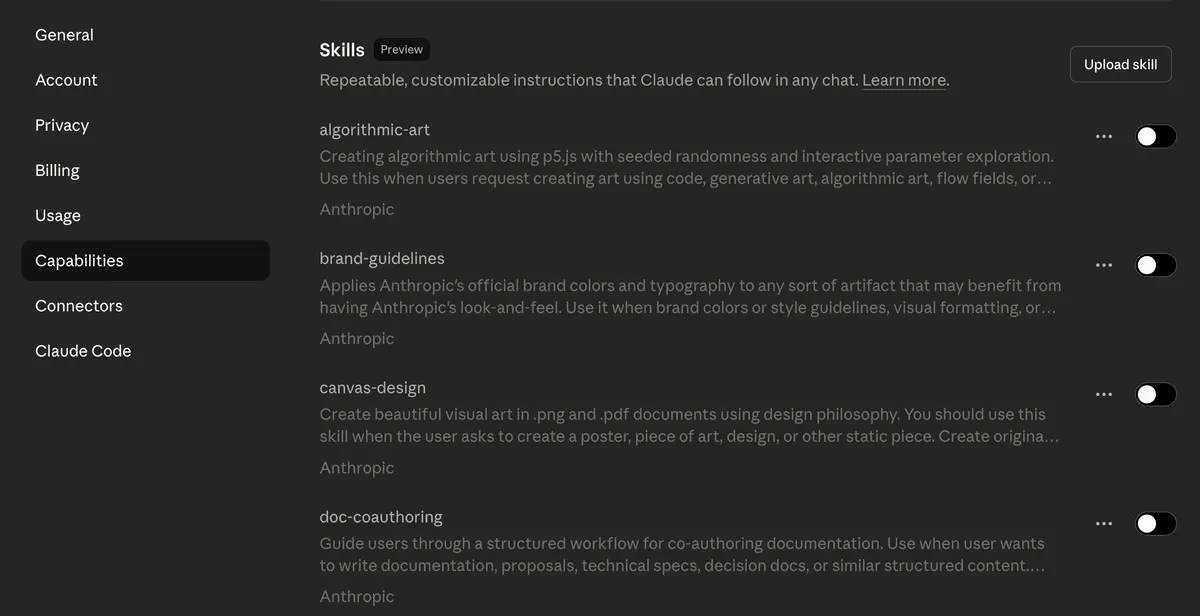
Claude Skills
Claude skills are folders of specialized knowledge that contain:
- instructions,
- documentation,
- best practices,
- examples, and
- specific guidance
for a task.
Skills free you from having to repeat yourself or use the same prompts endlessly. Claude will already have the information from the Skill.
For example, instead of always mentioning your brand color scheme whenever you need a presentation, the Skill will already provide all the context Claude needs. You could have another skill with resources about your company. By bringing the two together, you get an on-brand presentation on features of your product with minimal effort and without having to develop long forgettable prompts.
How Claude Skills work
Instead of re-explaining your brand guidelines, sales process, or coding standards in every conversation, you create a Skill once and Claude loads it automatically when needed.
Understanding the Skills architecture
Each Skill contains a SKILL.md file that defines what the Skill does and when Claude should activate it. Think of this file as a resume—it tells Claude: "I'm the brand guidelines expert" or "I handle sales follow-ups."
When you send Claude a request, it scans all available Skills by reading only their metadata (name and brief description). This scanning costs roughly 100 tokens per Skill—negligible compared to loading full instructions. If Claude determines a Skill matches your task, it loads the complete instructions, reference materials, and any executable code inside that Skill.
Traditional AI workflows force you to include all context upfront. Every conversation burns thousands of tokens explaining the same brand colors, tone guidelines, or process steps. Skills flip this model: Claude only loads what it needs, when it needs it. For a team running 1,000 AI requests daily, this cuts token costs by 60-90%.
This matters because some tasks demand deterministic outputs: exact calculations, specific formatting, consistent data structures.
LLMs are non-deterministic by design. Ask Claude to format a presentation five times, you'll get five slightly different layouts. But when a Skill contains a Python script that generates PowerPoint slides with exact brand specifications, you get identical output every time.
You ask Claude to create a LinkedIn carousel about your product. Claude recognizes this matches your "Brand Guidelines" Skill. It loads your brand colors, fonts, and logo files. Then it executes a Python script (python-pptx library) that builds a perfectly formatted carousel with your assets positioned exactly where they belong. The creative content comes from Claude's language model. The formatting precision comes from deterministic code.
Building your first Skill: Sales follow-up automation
Let’s make this concrete with a use case almost every B2B team recognises: post-call sales follow-ups.
Step 1: Define the Skill scope
Start a new Claude conversation and say:
"I want to create a Skill that handles sales follow-ups after discovery calls. After each call, I'll provide the transcript and some basic company info. The Skill should extract pain points, map them to our solution, draft a follow-up email, and suggest proposal talking points."
Claude will ask clarifying questions:
- What fields do you need in the input form?
- What's your preferred email tone?
- Should it reference specific product features or case studies?
Answer these to help Claude understand your requirements.
Step 2: Let Claude build the Skill structure
Claude generates a folder containing SKILL.md (the metadata file), detailed instructions for each task (pain point extraction, email drafting, proposal notes), and optionally some sample templates or reference materials.
The SKILL.md file might read:
"Sales Follow-Up Skill — Analyzes discovery call transcripts to extract pain points, generate personalized follow-up emails, and create proposal customization notes. Activates when user mentions: sales call, discovery transcript, follow-up email, proposal prep."
Step 3: Download and upload the Skill
Claude provides the Skill as a downloadable folder.
- Compress it into a ZIP file.
- Go to Claude Settings → Capabilities → Skills → Upload Skill.
- Select your ZIP file.
Claude now has access to this Skill across all conversations.
Step 4: Test and refine
Start a new conversation. Say:
"I just finished a discovery call with a recruitment company. Here's the transcript."
Paste the transcript and add company details (size, industry, AI maturity level). Claude recognizes the Sales Follow-Up Skill, loads it, and processes the transcript through each defined step.
Review the output:
- Does the pain point analysis capture the real issues?
- Is the email tone right?
- Are proposal notes actionable?
If something's off, return to the conversation where you built the Skill.
Say:
"When analyzing transcripts, prioritize stated problems over implied ones" or "Use a more conversational tone in emails—professional but friendly, no corporate jargon."
Claude updates the Skill instructions. Download the revised version, upload it again, and test.
Watch this workflow live in this video:
Connecting Skills to your business workflows
Skills work across Claude's ecosystem. Once you create a Skill, it's available in:
- Claude web chat
- Claude mobile apps
- Claude Code (command-line coding tool)
- Claude API (for custom integrations)
This means you build the Skill once and deploy it everywhere your team uses Claude.
Example: Customer service escalation
- Create a "Support Triage" Skill that analyzes incoming support tickets, categorizes urgency, identifies required expertise (technical, billing, product), and drafts initial responses.
- Customer service reps paste tickets into Claude.
- The Skill activates automatically, processes the ticket, and returns: severity level, routing recommendation, draft response, and suggested knowledge base articles.
- Reps review and send—cutting response time from 20 minutes to 3 minutes.
Example: Compliance checking
- Build a "Contract Review" Skill loaded with your company's legal requirements, risk tolerance levels, and standard clauses.
- Legal teams paste contract drafts into Claude.
- The Skill flags non-standard terms, missing clauses, and potential compliance issues.
- It doesn't replace lawyers, but it catches 80% of routine problems before human review—saving hours per contract.
What not to do when creating Claude Skills
Skills that are too broad
"Marketing Skill" that handles social posts, email campaigns, ad copy, and presentations. This bloats the Skill file and confuses activation logic. Split it into focused Skills: Social Media Skill, Email Campaign Skill, Ad Copy Skill. Each activates precisely when needed.
Insufficient activation keywords
If your Brand Guidelines Skill only activates when you say "apply brand guidelines," Claude won't load it when you say "make this look professional" or "create a branded carousel." Include diverse activation triggers: brand, branding, professional look, company style, visual identity, on-brand, etc.
No version control
Skills evolve. Your brand colors change. Your sales process updates. Maintain version numbers and change logs inside each Skill. When you update a Skill, note what changed and why. This helps when troubleshooting unexpected outputs.
How to measure the impact of Claude Skills
- Time saved per task. Measure how long a workflow takes manually versus with a Skill. Sales follow-ups drop from 30 minutes to 5 minutes? That's 25 minutes saved per call. For a rep handling 10 calls weekly, that's 4+ hours reclaimed weekly.
- Consistency scores. Review outputs for consistency. Do all sales emails follow the same structure? Do all presentations use correct brand assets? Skills should be able to enforce consistency.
- Adoption rate. Track how many team members actively use Skills. Low adoption signals training gaps or Skill design issues. High adoption (>70% of target users) validates that Skills solve real problems.
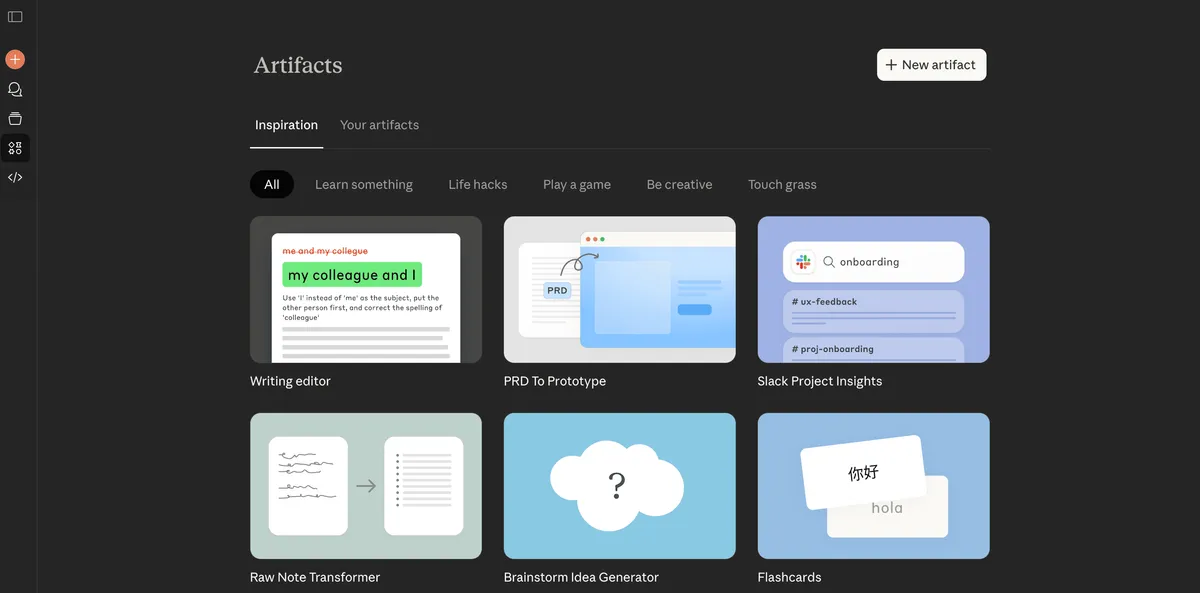
Claude Artifacts: How to build functional tools without code
Claude Artifacts let you turn a conversation into an interactive mini-app inside Claude’s interface. Unlike ChatGPT Canvas, Artifacts can embed AI capabilities inside the tool itself, turning static outputs into dynamic, AI-powered applications.
How Claude Artifacts work
Artifacts are live previews, not just documents
When you ask Claude to build something visual or interactive, it creates an Artifact—a split-screen interface with your chat on the left and the live app on the right. You see your tool running in real time as Claude builds it.
Claude creates an artifact when the content has the following characteristics:
- It is significant and self-contained, typically over 15 lines of content.
- It is something you are likely to want to edit, iterate on, or reuse outside the conversation.
- It represents a complex piece of content that stands on its own without requiring extra conversation context.
- It is content you are likely to want to refer back to or use later on.
Artifacts could be games, tools, calculators, internal apps, and the list goes on. Common examples of Artifacts include:
- Documents (Markdown or Plain Text)
- Code snippets
- Websites (single page HTML)
- Scalable Vector Graphics (SVG) images
- Diagrams and flowcharts
- Interactive React components
ChatGPT Canvas comparison
ChatGPT Canvas lets you edit code or documents with AI assistance. But you can't build a mini web app or have AI feature inside it to the power the application. But with Claude Artifacts, you can.
Example from real usage
A sales team built a call analysis tool as an Artifact. Reps paste call transcripts into the tool. The tool (powered by Claude's API embedded in the Artifact) extracts pain points, scores call quality, generates follow-up tasks, and suggest a strategy—all without leaving the Artifact interface. This wouldn't be possible in ChatGPT Canvas because you can't embed AI processing inside the Canvas.
How to build an Artifact
Start with a clear use case
Artifacts work best for tools you'll use repeatedly—calculators, form processors, data visualizers, mini-dashboards, simple games for engagement.
Let's build a customer feedback analyzer. Marketing teams receive feedback surveys but lack time to analyze patterns. We'll create an Artifact that processes raw feedback, identifies themes, and suggests action items.
Step 1: Describe what you need
Open Claude and say:
"Build an Artifact that analyzes customer feedback. I'll paste survey responses. It should identify common themes, sentiment trends, and suggest 3-5 action items based on the feedback."
Claude asks clarifying questions:
- How many responses will you typically analyze at once?
- Do you want sentiment scored numerically or categorically?
- Should action items prioritize by impact or ease of implementation?
Answer these to guide the build.
Step 2: Claude generates the Artifact
Within 30-60 seconds, Claude creates an Artifact with a text input area for pasting feedback, an "Analyze" button, and output sections for themes, sentiment, and action items. The Artifact appears in the right panel. You see it working immediately.
Step 3: Test with real data
Paste actual customer feedback. Click Analyze. Claude processes the input and returns structured results.
If the output format isn't quite right, tell Claude:
"Display sentiment as percentages, not just labels" or "Group themes by frequency."
Claude updates the Artifact code and regenerates the preview.
Step 4: Refine and iterate
- What happens if feedback is in bullet points versus paragraphs?
- What if someone pastes 500 responses instead of 50?
- Does the Artifact handle non-English feedback?
Identify issues and ask Claude to fix them:
"Add a character limit warning" or "Support Spanish and French feedback."
Artifacts vs. Custom GPTs vs. Skills
In practice, most teams end up with a hybrid setup. That’s normal and recommended. What matters is that the right tool is doing the right job.
Business applications of Artifacts
ROI calculator for sales
Input deal size, implementation scope, and timeline. The Artifact estimates ROI and payback period and suggests talking points reps can use on calls.
Hiring scorecard assistant
Paste interview notes and role requirements. The Artifact scores candidates across key competencies and suggests questions for the next round.
Expense review helper
Paste expense exports. The Artifact groups costs, flags outliers, and highlights potential policy violations.
How to mix Skills and Artifacts for maximum impact
Skills and Artifacts complement each other. Skills define what Claude knows. Artifacts define what tools you build with Claude's capabilities.
Example workflow: Product launch “command centre”
Create a Claude Skill named Product Launch Playbook Skill. In it, encode your standard launch process: messaging, channels, timelines, deliverables.
Launch a Claude Planner Artifact. Someone from your team inputs product name, target audience, launch date, and constraints. The Artifact:
- Generates a tailored launch checklist
- Suggests messaging angles and headline options
- Proposes a channel plan (email, social, partners, etc.)
Result: Every launch follows the same proven playbook, but adjusts to the specific product and audience.
This layered approach—Skills for intelligence, Artifacts for interfaces—lets non-technical teams build sophisticated automation without writing code or managing API integrations.
Key takeaways
The goal isn’t to crown “one perfect model”, but to build systems where AI:
- Handles the repetitive, structured parts of your work
- Respects your processes, guidelines, and constraints
- Gives your team more time for strategy, creativity, and relationships
Claude is a strong option when you want to:
- Work with long, complex inputs
- Build repeatable, reliable workflows
- Turn your best processes into Skills and Artifacts your whole team can use
Start small: build one Skill for a task you repeat weekly, or create one Artifact to replace a manual process. Iterate based on real outputs. Refine until it works without supervision. Then scale across your team.
Ready to start? Book a call with us today.
More Articles

The 5-Tool AI Stack Replacing 100+ Subscriptions for Small Businesses
Most small businesses are drowning in AI subscriptions they never chose. Here's how a lean five-tool stack — Claude, Notion, Google Workspace, Slack, and Mercury — replaced an entire category of software and headcount, without the overhead.

Building a 24/7 AI assistant with OpenClaw + Mac Mini: Is It Worth It?
A practical guide to running a 24/7 AI assistant on local hardware using OpenClaw and a Mac Mini — covering setup paths, real costs, security trade-offs, and how to decide if local AI is right for your business.

Claude Cowork: Easy AI Automation That Saves 20+ Hours Monthly
Discover how Claude Cowork automates file cleanup, inbox triage, and data entry to save your team 20+ hours monthly. Learn use cases, setup, and limitations.